HP Feeding Concept
Stress free weaning without ZnO and high revenues. Using a combination of high-quality premium protein and special fibres - HP 300 and HP FiberBoost
Have you made any changes to your diets after the ZnO ban or maybe lowered the CP levels in your diets? Then how is the performance of the animals after the CP reduction?
Many nutritionists reduce CP levels to cope with ZnO free diets. Other motives to use lower CP levels in nursery diets are to reduce feed costs and to control nitrogen excretion into the environment. However, reducing the crude protein content of nursery diets may be a costly decision as the risk exists that within the total amino acid (AA) absorption from a low CP diet some AA may fall under the required level for nursery pigs.
However, keeping protein levels brings the risk of too much fermentation in the hindgut and thus post weaning diarrhea (PWD). To avoid this from happening most measures are directed towards fixing the problem of pathogenic growth in the hindgut by means of antimicrobial or anti-inflammatory feed additives.
At Hamlet Protein we believe it is more effective to eliminate the cause of this pathogenic growth; the undigested protein going to the hindgut where it is fermented by various pathogens. Reducing the amount of excess protein reaching the hindgut using highly digestible protein, free of anti-nutritional factors (ANF's) in the form of HP 300 should be the first step.
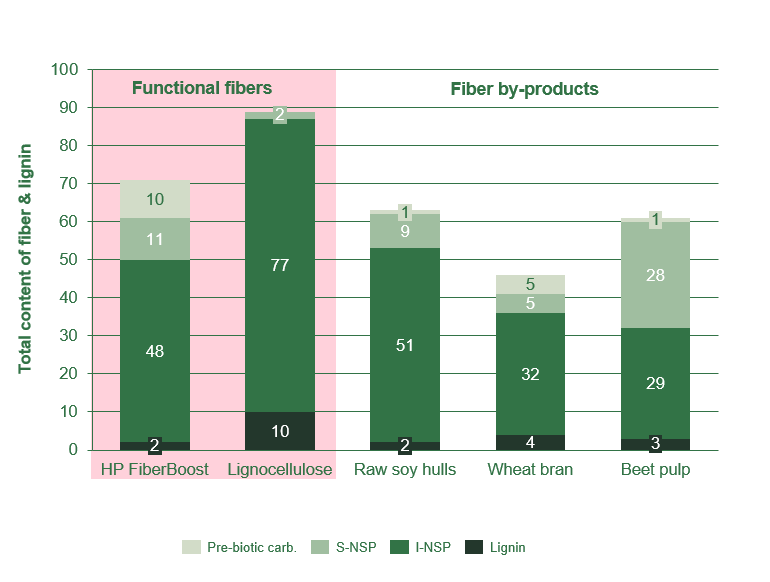
Improving the gut environment using a specialty fiber that contains both insoluble and soluble fibers as well as prebiotics; HP FiberBoost, is the second to support piglets’ resilience and gut health. Our HP FiberBoost is the only standardized fiber feed material that contains the combination of both fiber fractions and a high quantity of prebiotics especially formulated to improve gut health in swine.
Combining the unique properties of HP 300 with HP FiberBoost allows to keep high CP levels in nursery diets without losing performance.
By using HP 300, as many digestible amino acids as possible are supplied to the piglet within the chosen crude protein limit. Having the lowest ANF content ensures minimal loss of amino acids due to reduced digestibility or inflammatory processes. As a result, less excess protein goes to the hindgut whereby less fermentation by pathogens takes place which reduces scouring.
A fibre source combining prebiotic effects and benefits of insoluble fibres backs up gut health and helps the gut to withstand sanitary challenges. The value of the additional amino acids from the increased digestibility of HP 300 can be witnessed from an improved FCR and increased N retention.
HP FiberBoost is the ‘insurance’
Functional fibers have multiple beneficial effects on gut health and increase the resilience of the animals to withstand challenges. Soy hulls is a great fiber source but contains ANF’s and may contain mycotoxins.
HP FiberBoost is made from soy hulls that are carefully sourced to avoid mycotoxins. It is enzymatically processed to increase the prebiotics and combines benefits from both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Our enzymes hydrolyze specific linkages to make fibers easier accessible for microbiota in the hindgut. Prebiotic carbohydrates and nutrients that were encapsulated within the fiber matrix become available as substrate due to this process.
ZnO ban
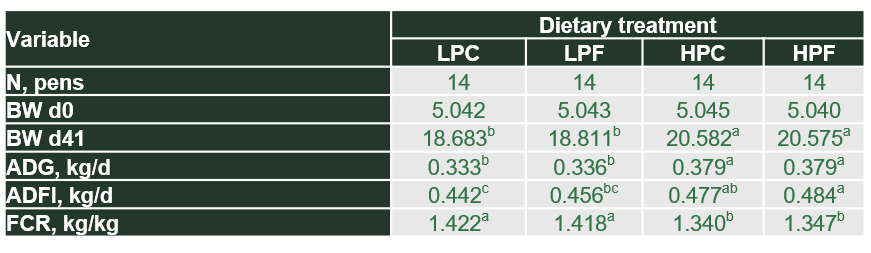
Lowering the CP level of the diet as a response to the ZnO ban comes at a cost in terms of reduced performance as FCR increases immediately when one of the AA’s falls below the minimum requirement. Reducing CP levels from 19 to 17% reduce piglet growth performance significantly, leading to increased FCR. Recent data show that the increase in FCR is clearly marked (1.42 at 17% CP vs 1.34 at 19% CP (see table 1)). Of course, this increases feed costs and reduces the revenue per pig. Reducing CP levels 2% costed 2.70 euros per pig in revenue in this trial.
Adding functional fiber (HP FiberBoost) to high protein diets maintains growth performance and feed conversion rates, but also increases piglet vitality and uniformity (table 1). These benefits improved the margin over feed costs with 1.40 euros per pig for high CP + HP FiberBoost vs high CP without HP FiberBoost.
So, keeping high protein levels in nursery diets without ZnO is very well possible when a highly digestible protein source (HP 300) is used and HP FiberBoost is added to the diet.
Table 1 Performance at day 41 post-weaning of pigs fed diet with low (LPC, 17% CP) or high (HPC, 19% CP) crude protein content without or with 4% HP FiberBoost (LPF or HPF).
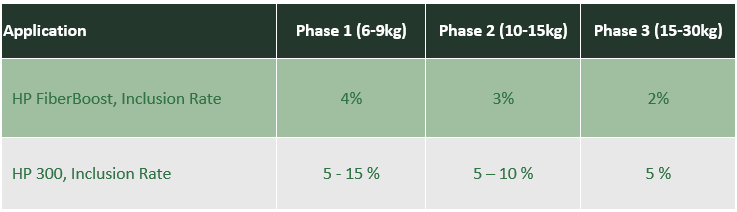
Application tips and tricks
Avoid reducing crude protein content of weaning diets below requirements.
- It increases the FCR
- It does not reduce feed costs
- It does not reduce nitrogen excretion per kg meat produced
Use HP Feeding Concept; combining high quality protein with prebiotic fibres
- The highly digestible protein avoids scouring
- The specialty fiber acts as an insurance to improve the resilience of the animals
As a result:
- Increased ADG
- Improved FCR
- Improved uniformity of piglets
- Reduced N excretion
- Improved economy
HP 300 AND HP FiberBoost. Stress free weaning = higher revenues
Combining the unique properties of HP 300 with HP FiberBoost allows to keep high CP levels in nursery diets without losing performance.
Vi visited swine farmer Søren Stenskrog to talk about his experience with our products.
Thank you to Søren Stenskrog - Swine farmer and Birgitte Bendixen Møller - Consultant Elite Opti for participating in this video.

Product benefits
Feed is the critical factor in animal production, accounting for up to 70% of total costs. Using HAMLET PROTEIN specialty soy proteins in young animal feed, you can optimize feed efficiency – and maximize your return on investment.
The key is their easy absorption by immature guts. Although added to feed for only a limited period in early life, our proteins have a strong carry-over effect on animal growth and performance. Feeding trials have documented a higher slaughter weight compared to animals fed standard soybean meal.
Our highly bioavailable proteins improve feed quality overall. That paves the way to reducing the total protein content – cutting the cost of your formulation.

